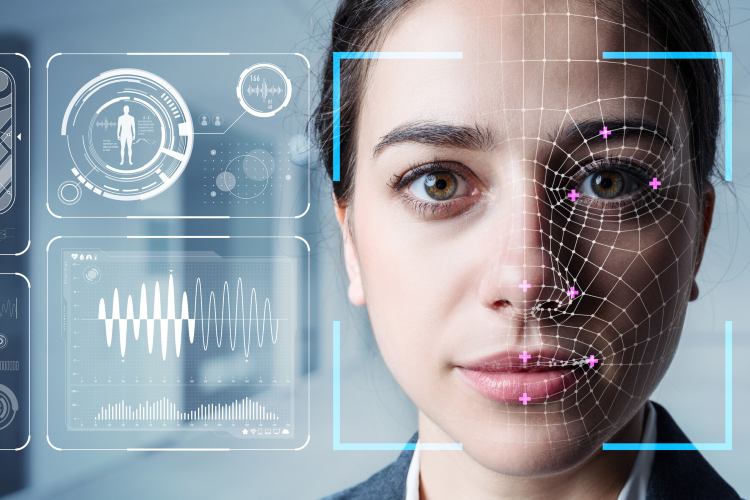
Biometrics refers to the measurement and analysis of unique physical or behavioural characteristics of an individual, such as fingerprints, iris patterns, facial recognition, and voice recognition, for the purpose of identity verification. Biometrics has gained popularity in recent years as a means of ensuring secure access to sensitive information and resources, and has become an increasingly important tool for enhancing security in various industries and applications.
In the context of security, biometrics is used to authenticate an individual's identity by comparing their biometric data to a reference template that is stored in a database. This template can be created from a variety of sources, including photos, videos, or even physical scans of a person's fingerprints or iris patterns. The process of matching the individual's biometric data to the reference template is performed by a biometric algorithm, which determines the degree of similarity between the two sets of data.
One of the main benefits of biometric security systems is that they are based on unique and unchangeable characteristics, making it difficult for a user to be impersonated or to gain unauthorised access to secure systems. This is in contrast to traditional forms of security, such as passwords, which can be forgotten, lost, or easily hacked. Additionally, biometrics provides a more convenient and efficient form of authentication, as users do not need to remember any additional information or carry any physical devices in order to access secure systems.
Another benefit of biometrics is that it can be used to create a multi-factor authentication system, which combines multiple forms of authentication, such as biometrics and a password, to provide a more secure and reliable form of authentication. This helps to mitigate the risks of unauthorised access and provides an additional layer of security against hackers and cyber criminals.
Biometrics is widely used in a number of different industries and applications, including law enforcement, border control, and financial services. For example, law enforcement agencies use biometrics to identify suspects, monitor criminal activity, and improve the accuracy of criminal investigations. Border control agencies use biometrics to quickly and accurately identify travellers and ensure that they are authorised to enter or leave the country. Financial services companies use biometrics to verify the identity of customers and to prevent fraud and unauthorised access to sensitive financial information.


.webp)